The Process
Follow these steps to help you through the process of finding the right car seat, installing it correctly, and keeping your child safe.
Find the right car seat
- Learn about the four car seat types
- Follow NHTSA’s car seat recommendations based on your child’s age and size
- Find and compare car seats and ease-of-use-ratings using NHTSA’s Car Seat Finder
Install your car seat correctly
- Understand the parts and tips used for installation
- Follow our detailed car seat installation instructions and videos
- Get your car seat inspected at a station nearest you
Keep your child safe in a car seat
- Register your car seat and sign up for recall notices to receive safety updates
Car Seat Safety Tips
How to Choose the Right Seat
Watch the video
Find The Right Car Seat
Car Seat Types
Learn about the four types of car seats, while keeping in mind the following tips:
- As children grow, how they sit in your car will change. Make sure you use a car seat that fits your child’s current size and age.
- Not all car seats fit in all vehicles. Make sure the car seat is the right fit for your vehicle (PDF, 1.77 MB). Test the car seat you plan to buy to make sure it fits well in your vehicle.
- Buy a car seat that can be installed and used correctly every time.
Rear-Facing Car Seat

The best seat for your young child to use. It has a harness and, in a crash, cradles and moves with your child to reduce the stress to the child's fragile neck and spinal cord.
Types
- Infant Car Seat (Rear-Facing only): Designed for newborns and small babies, the infant-only car seat is a small, portable seat that can only be used rear-facing. Most babies outgrow their infant seats before their first birthday. When that happens, we recommend that parents purchase a convertible or all-in-one car seat and use it rear-facing.
- Convertible Seat: As a child grows, this seat can change from a rear-facing seat to a forward-facing seat with a harness and tether. Because it can be used with children of various sizes, it allows for children to stay in the rear-facing position longer.
- All-in-One Seat: This seat can change from a rear-facing seat to a forward-facing seat (with a harness and tether) and to a booster seat as a child grows. Because it can be used with children of various sizes, it allows for children to stay in the rear-facing position longer.
Forward-Facing Car Seat

Has a harness and tether that limits your child's forward movement during a crash.
Types
- Convertible Seat: As a child grows, this seat can change from a rear-facing seat to a forward-facing seat with a harness and tether.
- Combination Seat: As a child grows, this seat transitions from a forward-facing seat with a harness and tether into a booster.
- All-in-One Seat: This seat can change from a rear-facing seat to a forward-facing seat (with a harness and tether) and to a booster seat as a child grows.
Booster Seat

Raises and positions a child so the vehicle’s lap-and-shoulder belt fits properly over the stronger points of a child’s body, the hips and across the chest.
Types
- Booster Seat With High Back: This type of booster seat is designed to boost the child’s height so the seat belt fits properly. It also provides neck and head support and is ideal for vehicles that don’t have head rests or high seat backs. This seat may ease the transition from a harnessed car seat by having a similar structure, and must be used with lap-and-shoulder seat belt.
- Backless Booster Seat: A backless booster seat is designed to boost the child’s height so the seat belt fits properly. It does not provide head and neck support. It’s only to be used in vehicles that have head rests or high seat backs and must be used with lap-and-shoulder seat belt.
- Combination Seat: As a child grows, this seat transitions from a forward-facing car seat with a harness into a booster seat. When transitioned to a booster seat, this seat may be used in vehicles that do not have head rests or high seat backs, but must be used with lap-and-shoulder seat belt.
- All-in-One Seat: This seat can change from a rear-facing car seat to a forward-facing car seat (with a harness and tether) and to a booster seat as a child grows. When transitioned to a booster seat, it must be used with lap-and-shoulder seat belt.
Seat Belt

Should lie across the upper thighs and be snug across the shoulder and chest to restrain your child safely in a crash. It should not rest on the stomach area or across the neck or face.
Find The Right Car Seat
Car Seat Recommendations
There are many car seat choices on the market. Use the information below to help you choose the type of car seat that best meets your child’s needs or print out NHTSA’s car seat recommendations for children (PDF, 370 KB).
- Select a car seat based on your child’s age and size, then choose a seat that fits in your vehicle, and use it every time.
- Always refer to your specific car seat manufacturer’s instructions (check height and weight limits) and read the vehicle owner’s manual on how to install the car seat using the seat belt or lower anchors and a tether, if available.
- To maximize safety, keep your child in the car seat for as long as possible, as long as the child fits within the manufacturer’s height and weight requirements.
- Keep your child in the back seat at least through age 12.
Recommended car seats based on your child's age and size
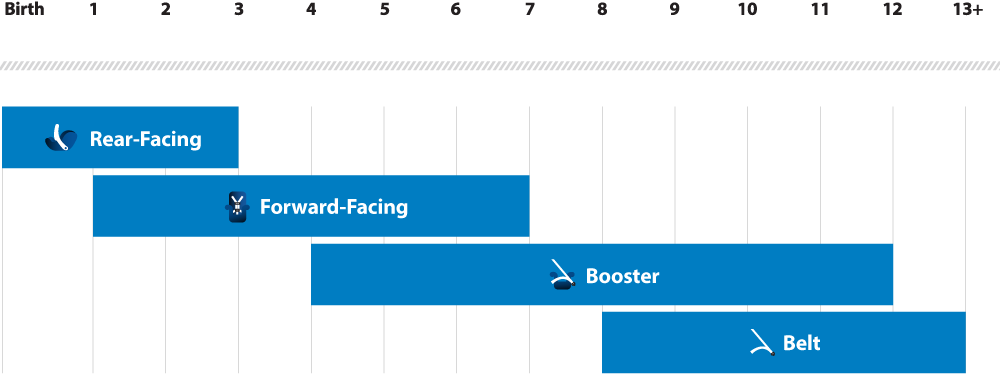
Rear-Facing Car Seat

Birth-12 Months
Your child under age 1 should always ride in a rear-facing car seat. There are different types of rear-facing car seats:
- Infant-only seats can only be used rear-facing.
- Convertible and all-in-one car seats typically have higher height and weight limits for the rear-facing position, allowing you to keep your child rear-facing for a longer period of time.
1 – 3 Years
Keep your child rear-facing as long as possible. It’s the best way to keep him or her safe. Your child should remain in a rear-facing car seat until he or she reaches the top height or weight limit allowed by your car seat’s manufacturer. Once your child outgrows the rear-facing car seat, your child is ready to travel in a forward-facing car seat with a harness and tether.
Forward-Facing Car Seat

1 – 3 Years
Keep your child rear-facing as long as possible. It’s the best way to keep him or her safe. Your child should remain in a rear-facing car seat until he or she reaches the top height or weight limit allowed by your car seat’s manufacturer. Once your child outgrows the rear-facing car seat, your child is ready to travel in a forward-facing car seat with a harness and tether.
4 – 7 Years
Keep your child in a forward-facing car seat with a harness and tether until he or she reaches the top height or weight limit allowed by your car seat’s manufacturer. Once your child outgrows the forward-facing car seat with a harness, it’s time to travel in a booster seat, but still in the back seat.
Booster Seat

4 – 7 Years
Keep your child in a forward-facing car seat with a harness and tether until he or she reaches the top height or weight limit allowed by your car seat’s manufacturer. Once your child outgrows the forward-facing car seat with a harness, it’s time to travel in a booster seat, but still in the back seat.
8 – 12 Years
Keep your child in a booster seat until he or she is big enough to fit in a seat belt properly. For a seat belt to fit properly the lap belt must lie snugly across the upper thighs, not the stomach. The shoulder belt should lie snugly across the shoulder and chest and not cross the neck or face. Remember: your child should still ride in the back seat because it’s safer there.
Seat Belt

8 – 12 Years
Keep your child in a booster seat until he or she is big enough to fit in a seat belt properly. For a seat belt to fit properly the lap belt must lie snugly across the upper thighs, not the stomach. The shoulder belt should lie snugly across the shoulder and chest and not cross the neck or face. Remember: your child should still ride in the back seat because it’s safer there.










